Govt programmes to push India’s water infra growth

Sustained capital outlay towards water supply and sanitation bodes well for the sector with numerous Government initiatives to aid healthy growth momentum.
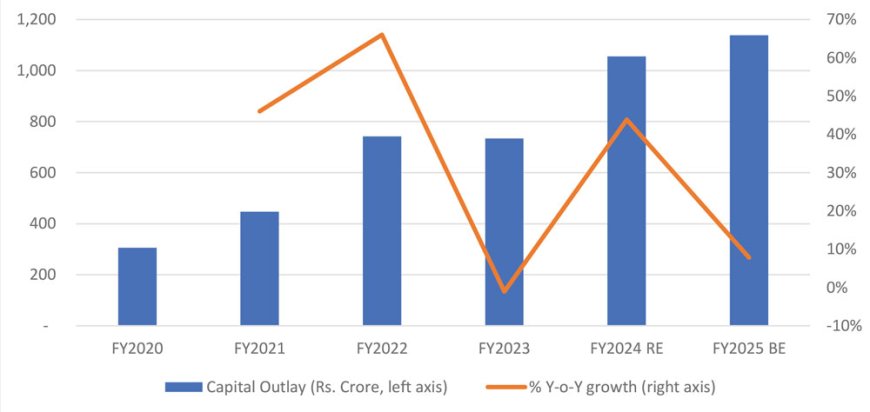
The capital outlay by 11 key Indian states towards Water Supply, Sanitation, Housing and Urban Development (WSSH&UD) rose at a healthy CAGR of 30% during FY2020-FY2025 budget estimates (BE) and is estimated to remain healthy, as is evident from the 8% budgeted increase in capital outlay for FY2025 (BE) over FY2024 revised estimates (RE). The EPC entities have witnessed strong order inflow in the water and sanitation segment in the backdrop of the Central Government’s ambitious schemes like Har Ghar Jal under JJM and the sewage treatment under the National Mission for Clean Ganga scheme. The players present in the water and sanitation segment are likely to witness healthy revenue growth in the medium term.
The Government of India has, over the last decade, initiated various schemes, missions and major policies in partnership with the state governments viz. Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM), Jal Shakti Abhiyan, National Water Mission (NWM), Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) and Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) to name a few. The construction activity in drinking and sewage water segment is poised to sustain its healthy growth momentum over the medium term, supported by healthy capital outlay and the Government’s numerous initiatives, some of which are detailed below:
Jal Jeevan Mission - Har Ghar Jal
The Har Ghar Jal Programme, one of the largest drinking water programmes in the world, implemented by the JJM under the Ministry of Jal Shakti, was launched with the aim to provide rural households with affordable and regular access to adequate supply of safe drinking water through taps. As on February 23, 2024, out of the targeted 19.27 crore households, 74.58% of households, have been provided with functional household tap connections (FHTC).
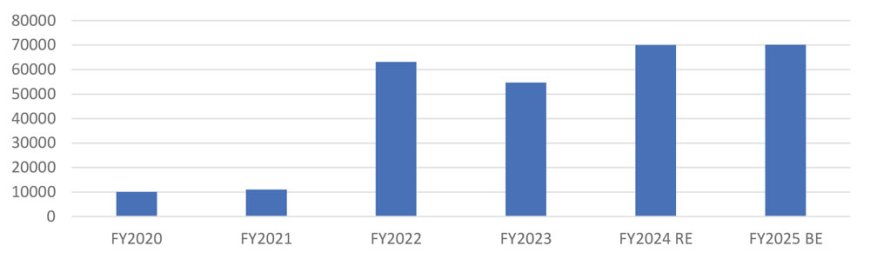
The budgetary allocation to JJM has grown at a CAGR of 48% during FY2020-2025BE, with the allocation in FY2025 BE being at a healthy Rs 70,162.9 crore.
There has been a visible increase in the annual release of funds by the Centre of Rs 60,713 crore to 29 eligible states/UTs for the implementation of JJM in FY2024. This is on the back of 36.83% YoY increase to Rs 54,744 crore in FY2023. Of the total funds released by the Centre in YTD FY2024, the top six states (Uttar Pradesh, Assam, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal and Karnataka) accounted for 66% of the share. As on date, 10 states/UTs have 100% of the households with tap water supply.
Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)
The JJM has two components - Rural and Urban - with the latter being covered under the AMRUT scheme. It is a flagship urban scheme of the Government of India as the first focused national water mission with the aim of making cities 'water secure' and providing functional water tap connections to all households. It is designed to provide universal coverage of water supply through functional taps to all households and sewerage/septage management in select 500 cities.
The AMRUT scheme’s prominence is reflected in the increasing proportion of AMRUT out of the total allocation to the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs at 13% and 17% in FY2024 RE and FY2025 BE, respectively, up from a mere 2% in FY2023. As on December 18, 2023, 1.87 crore new/serviced tap connections have been provided through AMRUT and in convergence with the state schemes and ~70% urban households are reported to have access to piped water supply.
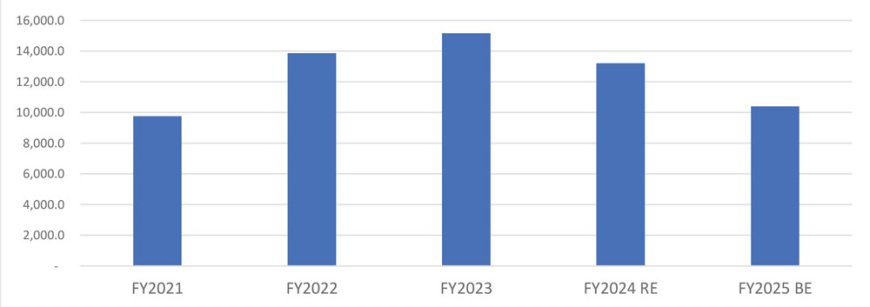
The budgetary allocation towards AMRUT and Smart Cities Mission has been fluctuating over the past few years, witnessing a YoY increase of 42% and 9% respectively in FY2022 and FY2023, only to reduce in the succeeding two years - by 13% and 21% in FY2024 revised estimates (RE) and FY2025 budget estimates (BE), respectively.
The average utilisation of the budgetary allocation to AMRUT has been encouraging with the total spent at Rs 45,304 crore out of the budgeted Rs 48,199 crore over FY2016-FY2023, showing an encouraging 81% utilisation of allocation.
Ministry of Jal Shakti
The Centre allocated Rs 77,877.10 crore to the Ministry of Jal Shakti in FY2025 RE, up 7.5% over FY2024 BE. It must be noted that this comes on the back of exponential YoY growth in the preceding two years – 30% in FY2024 RE and >400% in FY2023, with the latter coming on a relatively lower base of Rs 11,069.23 crore in FY2022. A further break-up of this allocation shows that with the increased focus towards the Department of Drinking Water & Sanitation, the proportion of allocation towards the Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation, has reduced significantly in the last three years ending FY2025 RE. The proportion of allocation towards the former has increased from almost nil in FY2022 to 84% in FY2025 RE with the balance share represented by the latter. This is also reflected in the order book addition of EPC companies with entities focused on JJM and drinking water-related projects witnessing strong order inflows and revenue booking in the last two to three years.

Chintan Dilip Lakhani







